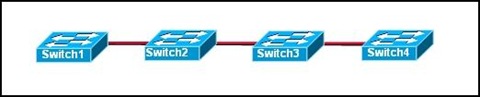
• client
• server
• pruning
• transparent
2. What are two characteristics of an extended ACL? (Choose two.)
• IP is used to specify TCP traffic only.
• IP is used to specify TCP and UDP traffic only.
• IP is used to specify all TCP/IP protocols including TCP, UDP, ICMP and routing protocols.
• Traffic can be filtered on source address only.
• Traffic can be filtered on source and destination address only.
• Traffic can be filtered on source and destination address, protocol, and specific port number.
3. Which two statements are true regarding a PPP connection between two Cisco routers? (Choose two.)
• LCP tests the quality of the link.
• LCP manages compression on the link
• Only a single NCP is allowed between the two routers.
• NCP terminates the link when data exchange is complete.
• With CHAP authentication, the routers exchange plain text passwords.
4. Assuming VLSM is not being used, what impact will adding the command ip route 172.16.64.0 255.255.240.0 serial0/0 have on a router that is already operational in a network?
• All packets with a destination address between 172.16.64.1 and 172.16.80.254 will be forwarded out serial0/0.
• All packets with a destination address between 172.16.64.1 and 172.16.255.254 will be forwarded out serial0/0.
• All packets with a destination address between 172.16.64.1 and 172.16.79.254 will be forwarded out serial0/0.
• All packets with a destination address between 172.16.0.1 and 172.16.64.254 will be forwarded out serial0/0.
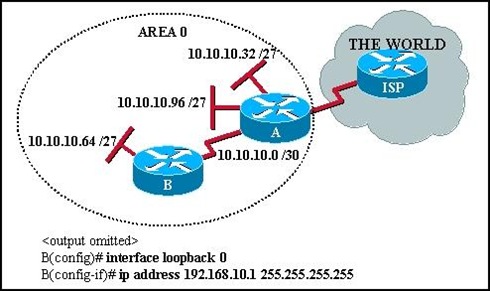
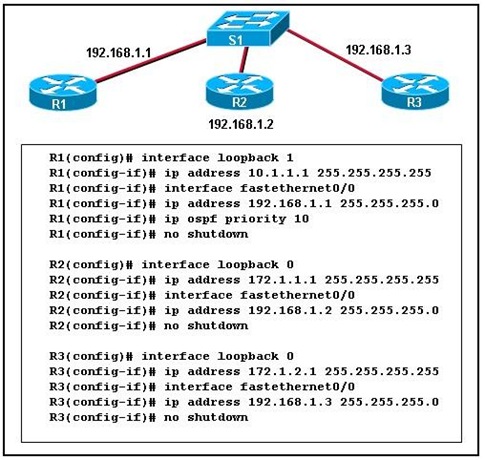
5.
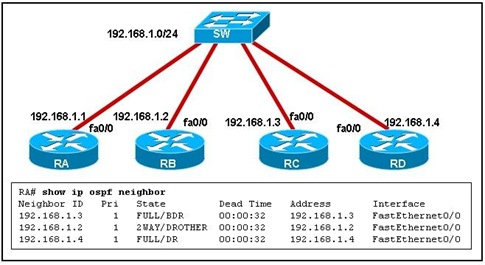
Refer to the exhibit. The network is using OSPF as the routing protocol. A network administrator issues the show ip ospf neighbor command to check the status of operation. Which statement is true?
• RB has the lowest priority value.
• RC and RD have the lowest router IDs on the network.
• RA has established adjacencies with all neighbor routers.
• RA and RB cannot form an adjacency because they are stuck in the 2-way state.
6. A sales representative is preparing to send sensitive information to corporate headquarters from a hotel room using the Internet. Prior to the trip, the IT staff made the necessary provisions to allow secure Internet access. What solution was implemented for the sales representative?
• VPN
• Frame Relay
• PPP with CHAP authentication
• PPP with PAP authentication
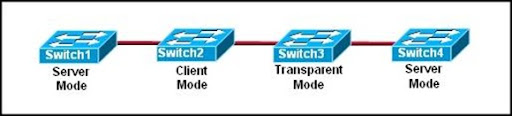
7.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator noticed that the VLAN configuration changes at SW2 did not propagate to SW3. On the basis of the partial output of the show vtp status command, what is the possible cause of the problem?
• VTP V2 mode is disabled.
• SW3 is configured as transparent mode.
• The number of existing VLANs does not match.
• The configuration revision number does not match.
8.
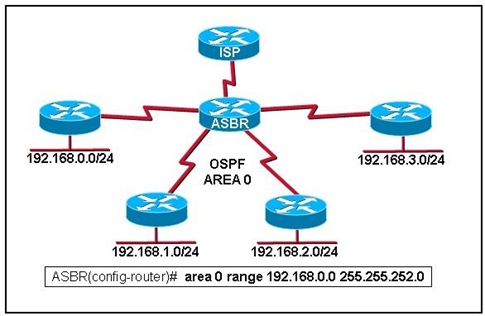
Refer to the exhibit. Because of continuing instability of one of the serial links in the OSPF network, a network administrator configures router ASBR as shown. Which two statements will be a result of this configuration? (Choose two.)
• Traffic intended for destinations across unstable serial links will be forwarded by ASBR even when the links are down
• A summary route of 192.168.0.0/22 will be advertised to the ISP router.
• Serial links in range 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 will be forced into a passive state.
• Networks connected to the unstable serial links will be placed in an unreachable state.
• Negative effects of route flapping will be reduced.
9. Which two criteria are used by STP to select a root bridge? (Choose two.)
• memory size
• bridge priority
• number of ports
• switch location
• switching speed
• base MAC address
10. A company is using a Class B IP addressing scheme and expects to need as many as 150 networks. What is the correct subnet mask to use with the network configuration?
• 255.255.0.0
• 255.255.240.0
• 255.255.254.0
• 255.255.255.0
• 255.255.255.128
• 255.255.255.192
11.
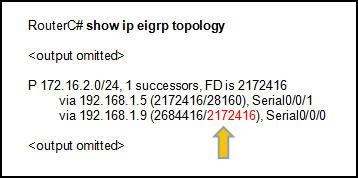
What is the term for the value 2172416 that is highlighted in the output of the show ip eigrp topology command?
• feasible distance of the successor
• reported distance of the successor
• feasible distance of the feasible successor
• reported distance of the feasible successor
12.
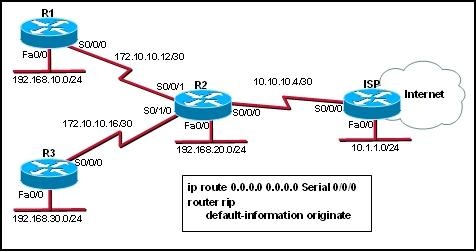
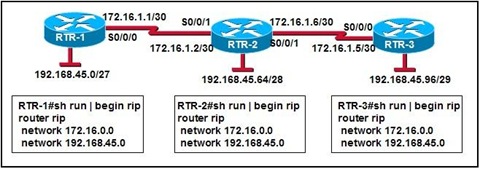
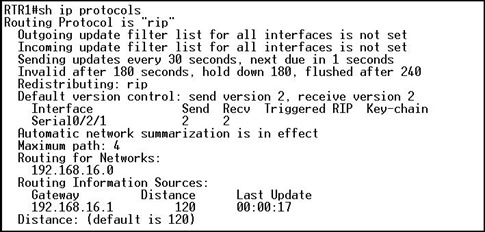
Refer to the exhibit. RIPv2 is configured in the network shown. Hosts in the network have access to all internal networks but do not have Internet access. On which router should the commands, shown in the exhibit, be added to provide Internet access for all hosts in the network?
• R1
• R2
• R3
• ISP
13. What do companies gain from the services performed at the enterprise edge?
• faster communication with server farms
• stronger security against malicious attacks
• faster communication with Internet destinations
• enhanced performance and reliability through VLANs and redundant trunk links
14.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator wishes to deny Internet access to all R2 LAN hosts, while allowing these hosts to reach all other devices on the company networks. Where the ACL shown in the exhibit should be placed to meet these requirements?
• R2: Fa0/0 inbound
• R1: S0/1/0 outbound
• R1: S0/0/1 inbound
• R2: S0/0/1 outbound
• R2: Fa0/0 outbound
15.

Refer to the exhibit. In what sequence (from first to last) does an OSPF router check the parameters listed when selecting the DR?
• C, B, A, D
• D, C, B, A
• A, B, C, D
• A, C, B, D
• B, C, A, D
16. What two statements are true regarding EIGRP tables? (Choose two.)
• A feasible successor route can be found in the topology table.
• A successor route can only be found in the routing table.
• The topology table shows whether a route is in the passive or active state.
• The routing table shows the amount of time elapsed since a router adjacency was formed.
• The neighbor table shows all adjacent Cisco devices.
• Administrative distance is shown as a column in the neighbor table.
17.

Refer to the exhibit. Assuming that all three routers are configured with the EIGRP routing protocol and sharing information, what information can be gathered from the show command output?
• Router B has EIGRP adjacencies with both router A and C.
• Router B has a fully converged topology table.
• Router B has not formed an adjacency with router A.
• Router B has not formed an adjacency with router C.
18. Which three statements are true about RSTP? (Choose three.)
• RSTP can fall back to STP to provide support for legacy equipment.
• RSTP and STP have the same number of port states.
• Like PortFast and UplinkFast, RSTP is a proprietary protocol.
• RSTP takes up to 50 seconds to converge.
• RSTP requires a point-to-point, full-duplex connection.
• RSTP views all ports that are not discarding as part of an active topology.
19.

Refer to the exhibit. A network support technician has been asked to set an IP address on one of the FastEthernet interfaces on a new router. What is causing the interface to reject the address?
• The IP address is already in use.
• The technician is using a network address.
• The technician is using the wrong subnet mask for /26
• The technician must enable VLSM on the interface.
20.
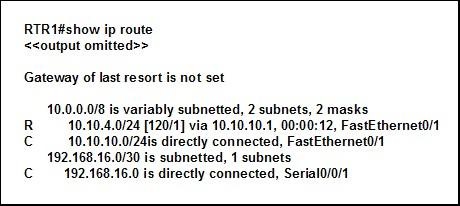
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator enters the command ip route 10.10.4.16 255.255.255.248 s0/0/1 into the router. What will be the result of this configuration?
• A static route pointing to 10.10.4.16/29 is placed into the routing table.
• A static route to 10.10.4.16/29 is placed into the routing table if interface FastEthernet0/1 goes down.
• A static route pointing to 10.10.4.16/29 is only placed into the routing table if the route to 10.10.4.0 is removed.
• A static route is not placed into the routing table because a RIP route that includes the destination network already exists.
21.

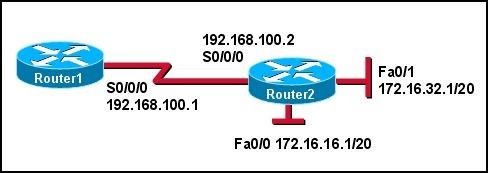
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is connected to the Internet through its serial 0/0/0 interface. Hosts on the 192.168.100.0/24 LAN on R1 cannot communicate with hosts on the Internet. What two NAT configuration issues might explain this failure? (Choose two.)
• The ip nat pool command has not been applied correctly.
• The inside interface has not been defined on R1.
• The access list does not include the group of IP addresses that are supported by the inside network.
• The ip address that is assigned to the serial 0/0/0 interface is incorrect
• The outside interface has not been defined on R1.
22.

Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are connected via serial interfaces. Both interfaces show that there is Layer 2 connectivity between them. The administrator verifies that CDP is operational; however, pings between the two interfaces are unsuccessful. What is the cause of this connectivity problem?
• no set loopback
• incorrect subnet mask on R2
• incompatible bandwidth
• incorrect IP address on R1
• incompatible encapsulation
23. Which two statements describe how the information contained in a BPDU is used by a switch? (Choose two.)
• to set the duplex mode of a redundant link
• to activate looped paths throughout the network
• to determine the root bridge
• to prevent loops by sharing routing tables between connected switches
• to determine which ports are placed in forwarding mode
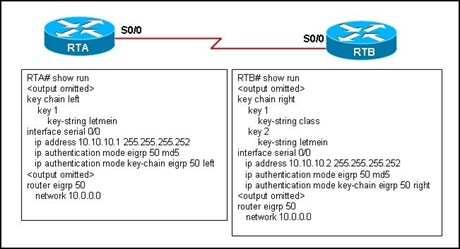
24. When MD5 authentication is used for OSPF routing protocol authentication, what two facts are known about the key? (Choose two.)
• The key passes between routers in plain text.
• The key is used to help generate an encrypted number for authentication.
• The key passes between routers in encrypted form.
• The key is never transmitted.
• The key can be captured by using a packet sniffer.
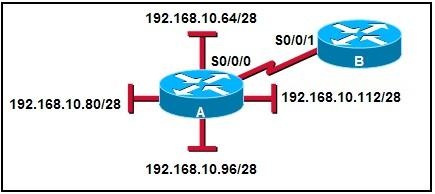
25.
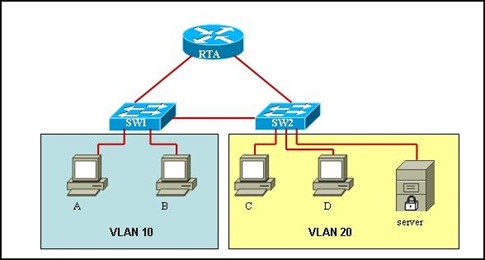
Refer to the exhibit. If router RTA fails, which statement is true?
• Hosts A and B can reach each other, but cannot reach hosts C and D or the server.
• No host can reach any other host.
• Hosts A, B, C, and D can reach each other, but cannot reach the server.
• All hosts can reach each other.
26. Which command should a network administrator issue to disable default summarization in an EIGRP network?
• Router(config-router)# null 0 route
• Router(config-if)# no ip summary-address
• Router(config-router)# no ip summary-address
• Router(config-if)# no auto-summary
• Router(config-router)# no auto-summary
27.

Refer to the exhibit. Users on the 172.30.20.0/24 network are unable to access any of the servers located on the 192.168.0.0/23 network. Given the network topology and OSPF configuration, what two problems exist in this network? (Choose two.)
• There is a routing loop occurring between all three routers.
• There is a network statement missing.
• Network 172.30.20.0 has an incorrect wildcard mask.
• The OSPF Area configuration is incorrect.
• /23 is an invalid subnet mask for the 192.168.0.0 network.
28.

Refer to the exhibit. Which IP addressing scheme would be correct for the network?
• H1-172.18.0.10/16
H2-172.18.0.11/16
H3-172.18.0.12/16
• H1-172.18.0.10/16
H2-172.19.0.10/16
H3-172.18.0.11/16
• H1-172.18.0.10/16
H2-172.18.0.11/16
H3-172.19.0.11/16
• H1-172.18.0.10/16
H2-172.19.0.11/16
H3-172.19.0.11/16
29.
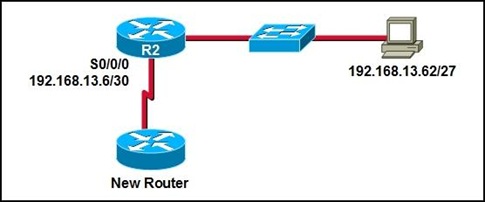
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is adding a new router to the network. The IP address 192.168.13.6/30 has been assigned to the connecting serial interface on R2. What IP address must the administrator assign to the serial interface of the new router?
• 192.168.13.4/30
• 192.168.13.5/30
• 192.168.13.7/30
• 192.168.13.58/30
• 192.168.13.61/27
• 192.168.13.63/27
30. After comparing a previous baseline to current network statistics, the network engineer has discovered a significant increase in unwarranted traffic to the extranet. Which two steps simplify administration and control the unwanted traffic? (Choose two.)
• define an ACL at the distribution layer to isolate packets
• add an ACL at the router in the enterprise edge to block the traffic
• deploy a Layer 3 switch to contain broadcasts
• connect remote locations directly to the intranet
• configure all hosts with the same default gateway to eliminate unnecessary broadcasts
• deploy one core ISP router to reduce the delay in path determination
31. Which statement is accurate about the CIR in Frame Relay?
• It is important to purchase a CIR that matches the highest bandwidth requirements of the enterprise.
• The CIR can be no lower than the port speed of the local loop.
• The CIR defines the contracted maximum rate available from the service provider on the Frame Relay circuit
• It is possible to burst over the CIR if bandwidth is available.
32. A sales representative is using a wireless connection to make a VoIP call. Which protocol will be used to transport the voice packets?
• TCP
• UDP
• PPP
• HDLC
33. A network administrator wants to deny responses to ping requests. Which ACL statement denies ping responses while not affecting other traffic?
• access-list 123 deny tcp any any eq 80
• access-list 123 deny tcp any any eq 20
• access-list 123 deny tcp any any eq 21
• access-list 123 deny icmp any any echo-reply
• access-list 101 deny tcp any any established
34. Why would a network administrator want to limit the size of failure domains when designing a network?
• to eliminate the effects of Ethernet collisions
• to reduce the impact of a key device or service failure
• to reduce the impact of Internet congestion on critical traffic
• to eliminate the need to block broadcast packets at the edge of the local network
35. What are two benefits of implementing VLANs in an enterprise network? (Choose two.)
• eliminates the need for a Layer 3 device
• provides segmentation of broadcast domains
• allows for the propagation of broadcasts from one local network to another
• allows for the logical grouping of devices despite physical location
• prevents issues such as broadcast storms by ensuring a loop free environment
36. Which three IP addresses are valid host addresses in the 10.200.0.0/20 network? (Choose three.)
• 10.200.11.69
• 10.200.16.1
• 10.200.0.255
• 10.201.0.55
• 10.200.15.240
• 10.200.30.29
37.
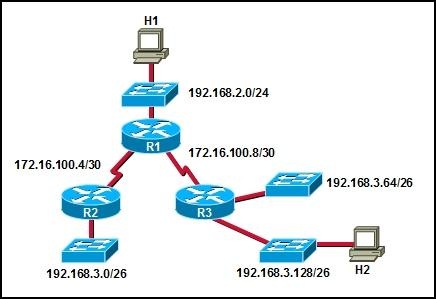
Refer to the exhibit. Assuming that the RIPv1 routing protocol is enabled and that all networks are being advertised, which statement is true?
• All packets from H1 that are destined to H2 will arrive at H2.
• None of the packets from H1 that are destined to H2 will arrive at H2.
• Approximately half the traffic from H1 that is destined to H2 will reach R3.
• Some of the packets from H1 that are destined to H2 will be sent to the switch that is connected to network 192.168.3.64/26.
38.

Refer to the exhibit. Which route will appear in the routing table?
• R 10.10.4.0/24 [120/1] via 10.10.10.1, 00:00:12, FastEthernet0/1
• R 10.10.4.0/24 [120/1] via 10.10.20.1, 00:00:12, FastEthernet0/0
• R 10.10.4.0/24 [120/2] via 10.10.20.1, 00:00:12, FastEthernet0/0
• R 10.10.4.0/24 [120/3] via 10.10.30.1, 00:00:12, FastEthernet1/0
• R 10.10.4.0/24 [120/1] via 10.10.30.1, 00:00:12, FastEthernet1/0
39.

Refer to the exhibit. Server7 has been added to the server farm network. The hosts can ping Servers 2 and 3 and Server2 and Server3 can ping each other. Server7 cannot ping the other servers connected to the switch. What is the cause of this problem?
• The Fa0/1 port on the switch should be in access mode.
• The switch IP address is not on the same subnet as Server7.
• The switch port used for Server7 is not in the same VLAN as Server2 and Server3.
• The Fa0/0 interface of the router has not been configured for subinterfaces to support inter-VLAN routing.
40. What will be the two wildcard masks required in an extended access list statement that blocks traffic to host 192.168.5.45 from the 172.16.240.0/27 network? (Choose two.)
• 0.0.0.0 5
• 255.255.240.0
• 255.255.255.255
• 0.0.31.255
• 255.255.255.240
• 0.0.0.31
41. If a modem is being used to connect to an ISP, which WAN connection type is being used?
• leased line
• cell switched
• circuit switched
• packet switched
42.
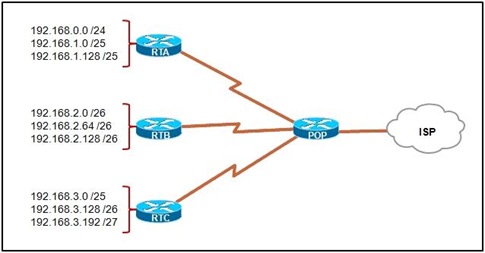
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator must manually summarize all IP addresses on the POP router for the ISP. Which one is the correct summary address?
• 192.168.0.0/22
• 192.168.0.0/23
• 192.168.0.0/24
• 192.168.0.0/25
43.
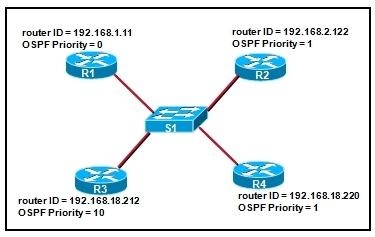
Refer to the exhibit. OSPF is enabled and the network has completely converged. Which two routers will be designated as DROTHER routers? (Choose two.)
• R1
• R2
• R3
• R4
44.

Refer to the exhibit. What two conclusions can be drawn from the displayed output? (Choose two.)
• A packet with a destination IP address of 172.20.1.14 will exit the router via the Serial 0/1/0n interface.
• The default administrative distance for EIGRP has been changed.
• Network 172.20.1.4 can be reached through two possible routes of equal cost.
• The addresses on this network were created using VLSM.
• The router connected to Serial 0/1/1 is advertising four separate routes through EIGRP to this router.
45.

Refer to the exhibit. What two pieces of information can be gathered from the output of this command? (Choose two.)
• 172.16.16.0/20 is a manually summarized route.
• All subnets are being advertised because default summarization was disabled.
• The output verifies that EIGRP is advertising only the networks in the same AS.
• The 172.16.1.0/24 network is directly attached to the router that produced this output.
• The Null0 interface indicates that this is not an actual path, but a summary for advertising purposes.
46.

Refer to the exhibit. What three facts represent the result of DR and BDR elections in this OSPF network? (Choose three.)
• RTC will be the DR of 10.5.0.0/30
• RTD will be the BDR of 10.5.0.0/30.
• RTD will be the DR of 10.4.0.0/28.
• RTB will be the BDR of 10.7.0.0/28.
• RTB will be the DR of 10.7.0.0/28.
• RTA will be the BDR of 10.4.0.0/28.
47.

Refer to the exhibit. Internet access is crucial for the company network shown. Internet access is provided by two ISPs. ISP1 is the primary provider and ISP2 is the backup provider. The network administrator configures BorderR as the border router so that in normal operations, all Internet traffic goes through ISP1. However, if the link to ISP1 fails, then BorderR will automatically forward Internet traffic to ISP2. The administrator configures two default routes:
BorderR(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.1 200
BorderR(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.1
However, when the administrator issued the show ip route command to verify the configuration, only the second default route is in the routing table. Why is the first default route not showing?
• The first configuration command overwrites the second command.
• The first default route will be installed into the routing table if there is traffic with an IP address that is destined for the 192.168.100.0 network.
• This is expected because the link to ISP1 is active. If the link to ISP1 goes down, then the first default route will be installed into the routing table.
• The first default route cannot be installed into the routing table unless the administrator manually disables the second default route with the no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.1 command.
48.
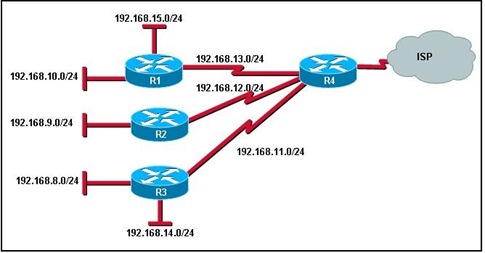
Refer to the exhibit. If R4 is announcing all shown internal networks as a summary address to the ISP, which summary address will be most specific?
• 192.168.1.0/22
• 192.168.4.0/21
• 192.168.6.0/23
• 192.168.8.0/21
• 192.168.4.0/22
49. Which two statements are true about the native VLAN on a switch? (Choose two.)
• It requires a special VLAN ID tag.
• It is unable to be changed to a different VLAN.
• Untagged traffic slows the switching process down
• The native VLAN defaults to VLAN 1 on Cisco Catalyst switches.
• Untagged frames that are received on a trunk become members of this VLAN
50.

Refer to the exhibit. A company has recently installed a new switch (S2) into their network.After several minutes, the network administrator notices that the new VLAN information is not being propagated to the new switch. Given the show vtp status command output, what is the possible problem that prevents the information from being received by the new switch?
• VTP version mismatch
• VTP domain name mismatch
• VTP revision number mismatch
• Time synchronization problems
51.

Refer to the exhibit. All routes in the exhibit are available to a router. Which two routes will be placed into the routing table? (Choose two.)
• A
• B
• C
• D
• E
• F
52.
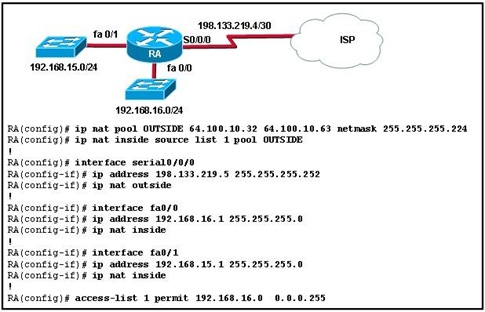
Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the command: RouterA(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255?
• It identifies traffic on all inside interfaces to be translated and given access to the ISP router.
• It identifies traffic from the fa0/1 interface to be translated and given access to the ISP router.
• It allows traffic from the ISP to reach all of the inside interfaces.
• It identifies traffic from the fa0/0 interface to be translated and given access to the ISP router
• It allows traffic from the ISP router to the fa0/1 interface.
53. The headquarters of a corporation uses static routes to connect to three branch offices. What are two advantages of using static routes for the WAN connections? (Choose two.)
• Static routes are more secure.
• Static routes converge faster.
• Static routes have higher administrative distances than dynamic routing protocols.
• The metrics of a static route need adjusting only if the bandwidth of the WAN connection changes.
• They are more stable and less susceptible to network changes in the interior gateway protocol.
54. What are two ways VLAN memberships can be created in an enterprise network? (Choose two.)
• manually configuring the switch ports to be part of a VLAN
• allowing the user to choose a specific VLAN through a GUI menu
• configuring the switch to allow VLAN membership based on NetBIOS association
• implementing an access list that specifies which devices are placed into specific VLANs.
• associating MAC addresses to specific VLANs in a VLAN management policy server database
• manually configuring the host devices to be part of a VLAN
55. Which two statements are true about RIPv1 and RIPv2? (Choose two.)
• Both versions broadcast updates on port 520.
• Both versions send the subnet mask as part of the update.
• By default, both versions will receive RIPv1 and RIPv2 updates.
• Both versions support the features of split horizon and poison reverse
• By default, both versions automatically summarize routes.
• RIPv1 has a higher AD than RIPv2 has.
56. Which bandwidth allocation technique minimizes bandwidth waste by reallocating unused time slices to communicating users?
• VPN
• NCP
• TDM
• STP
• STDM
57.
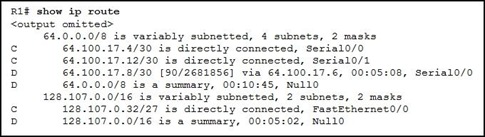
Refer to the exhibit. What is represented by the Null0 route for the 128.107.0.0 network?
• a child route that is defined
• a parent route that is defined and sourced from a physical interface
• a summary route for advertising purposes, not an actual path
• the result of the no auto-summary command on a router
58. If an authentication protocol is configured for PPP operation, when is the client or user workstation authenticated?
• prior to link establishment
• during the link establishment phase
• before the network layer protocol configuration begins